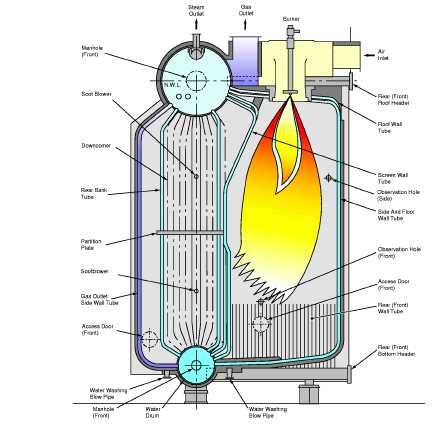
In a marine boiler, oil fired burner is normally used. Diesel or heavy fuel oil is used as burning fuel. The fuel to be used has to be clean and in correct temperature and viscosity for rapid combustion. This is to ensure the fuel to be at right atomization that will turn the fuel into micro droplets for efficient combustion.
Temperature is a critical factor as a lower than the normal temperature will lead to increase in the size of droplet resulting in poor combustion producing soot and smoke. If the fuel temperature is too high, the droplets can be too small leading to rapidly burning of the fuel near the burner tip. For a Marine Boilers, three basic types of burners are used.
1. PRESSURE JET BURNER
2. AIR OR STEAM BLAST ATOMISER
3. ROTARY CUP BURNER
2. AIR OR STEAM BLAST ATOMISER
3. ROTARY CUP BURNER
PRESSURE JET BURNER:
The main purpose of boiler burner is to break the oil into fine droplets i.e. to atomize the fuel in correct manner so that efficient combustion can be achieved. In pressure jet burner, an orifice or nozzle is fitted at the end of a pressure tube which atomizes the fuel in to fine droplets.
Atomization of fuel also depends mainly on the flow rate of the fuel from the burner’s end. The difference in the pressure of the fuel before and after the nozzle controls the flow-rate of the fuel from burner. Hence, if the flow rate of the fuel from burner is reduced to 50%, it will affect the atomization by a drop of 25%. To overcome this problem, this type of burner is supplied with different size of nozzle (having different diameter of orifice), which can be interchanged as per the flow rate of the fuel which mainly depends on the boiler load.
The fuel pressure required for pressure jet burner may vary from 7 bar to 15 bar depending upon the design of burner and load of the boiler. The maximum required viscosity at the burner inlet is normally 15 cst and both diesel and heavy oil can be used as a fuel.
Advantage of Pressure jet burner:
- Simple in construction
- Economical in maintenance
- Variety of sizes for different boiler load
- Can be accommodated in all type o furnca
- Produces variety of flame: short and fat, long and thin
Disadvantage:
- Limited turndown ratio for some nozzle size- 2:1
- Nozzle hole prone to frequent clogging
- This burner requires highest oil- pre heat treatment
- Nozzle cleaning to be carefully done as it can be damaged easily
- Requires frequent maintenance
- Inefficient at high load boilers
AIR OR STEAM BLAST ATOMISER:
This type of burner is similar in working as pressure jet, with an addition of high pressure steam supply arrangement incorporated in it. The oil is thus sprayed in the path of this high pressure air r steam which helps the fuel for atomization. Normally air is used during the initial starting of burner and then steam take over the operation. A convergent divergent nozzle is used to convert the pressure energy to kinetic energy which results in a high velocity jet of steam which enables atomization of oil which is sprayed in its path.
The steam side have tangential nozzle which provides rotatory motion to the fuel to ensure efficient combustion.
The fuel pressure required for pressure jet burner may vary from10 bar to 21 bar depending upon the design of burner and load of the boiler. The maximum required viscosity at the burner inlet is normally 15 cst and both diesel and heavy oil can be used as a fuel
Advantages:
- Robust construction
- High Turndown ratio of 4:1
- Efficient combustion over whole firing range
- Air fuel ratio can be adjusted for achieving efficiency
- Good combustion of heavy fuel oil
Disadvantages:
- combustion depends on steam/ air supply
- Additional maintenance of connections and piping for air and steam
ROTARY CUP BURNER
As the name suggest, this burner comprises of a burner nozzle which is covered by a rapidly rotating cone. The fuel oil is carried on to a nozzle which is centrally located within the rotating cone. As the fuel oil moves along the cup due to absence of centripetal force, the oil film becomes thinner in its course as the circumference of the cup increase. Ultimately, the fuel is discharged from the tip of the rotating cone in the form of fine atomized spray.
The atomization achieved in the rotating cup burner has very high turndown ration as compared o pressure jet burner because atomization is produces by rotating cup rather than pressurizing the fuel supply to nozzle.
Advantages:
- Good turndown ratio of better than 4:1.
- Good atomization of heavy fuel oils.
- Lowest oil pre-heat temperature required for atomization.
- No high pressure fuel in the line
- Disadvantages:
Complex in construction
Costly to maintain.
Electrical consumption and connections required for the
cup drive.
Pilot or Ignition Burner:
In some marine boiler with main burner firing in heavy fuel oil, it is very difficult to initially start the boiler with main burner. For start up of the boiler, a separate pilot or ignition burner is provided which uses diesel oil as a fuel. This enables the pilot burner to ignite even at the coldest condition the ship faces at sea.
The Pilot burner has a separate diesel oil piping and pump. The heat source is provided by two electrodes igniting the pilot flame, which are fitted to a high voltage ignition transformer. The pilot burner is allotted with a limited period of ignition during which it acts as a source of heat for main burner and once the time is over, the pilot flame goes off.
A pilot burner consists of a detachable nozzle with fine holes to atomize the diesel fuel for instant ignition. The nozzle to be cleaned at regular interval and operation of pilot burner checked for atomization.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Reference: